Your body protects you in many ways from getting hurt. Symptoms of cough and rash are among those methods of your body that are used for protection. Coughing helps in clearing your lungs or throat of irritating substances and makes your breathing easier. Coughing may also indicate that you are suffering from a medical illness. Similarly, a rash is a reaction of the skin to an irritating substance or any underlying medical illness. The appearance of a rash may vary. It may be red, blister-like or scaly.
What Are the Causes of Cough with Rash?
Cough and rash usually indicate an underlying medical illness including viral, fungal or bacterial infection. Some diseases that have rash and cough as symptoms are described below:
-
Scarlet fever
Scarlet fever is a type of infection that may develop in persons suffering from strep throat. It is caused by Streptococcus bacteria (group A), which may live in your nasal passages and mouth. The infection is contagious and may spread by contacting droplets of an infected person’s cough or sneeze. You can also get infection by eating or drinking from an infected person’s utensils.
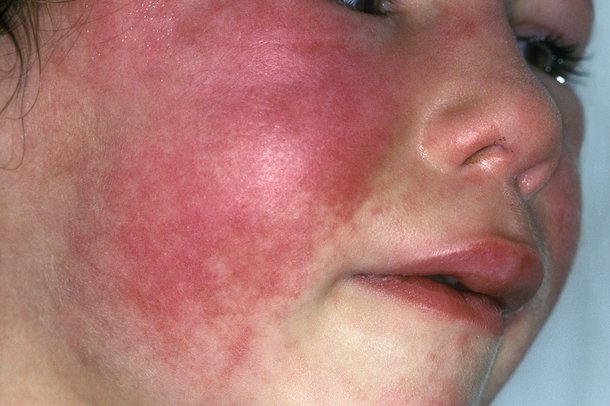
Scarlet fever affects children in the age group of 5 to 15 years. The symptoms are:
- Bright red colored rash that occurs on the body
- High fever
- Sore throat
- Flushed face
- Chills
- Headache
- Vomiting and nausea
- Swelling of tonsils
- Swelling of glands behind the neck
- Strawberry tongue
Treatment
Antibiotics are given to treat scarlet fever. OTC medicines such as ibuprofen and aspirin can be given to reduce fever. Your kid’s physician may also prescribe painkillers to relieve pain due to sore throat. Your child can do gargles with warm salt water to soothe swollen tonsils. You should also encourage your child to drink lots of water to prevent dehydration. Give your child broth based soups and warm teas to soothe their throat. They can use over-the-counter anti-itch gel or cream to alleviate itching of the rash. They can suck throat lozenges. Use air humidifier to relieve irritation of throat due to dryness of air.
How to prevent Scarlet fever
- Practice good hygiene. Wash your hands often.
- Cover your nose and mouth while coughing or sneezing.
- Avoid sharing drinking glasses and utensils with others.
-
Measles
Another disease that has cough and rash as symptoms is measles. Measles is a respiratory tract infection caused by a virus. It is a very contagious illness, which can spread when a non infected person comes in contact with an infected person’s saliva and mucus. The infection can also be released into the air by sneezing and coughing. You can also get infected by sharing utensils with an infected person. Measles is one of the leading causes of death among children.
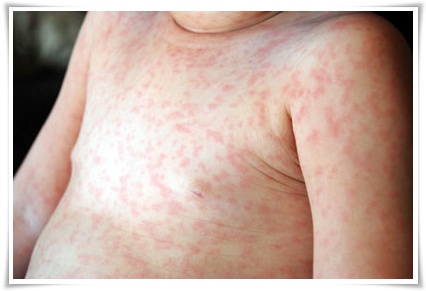
The symptoms are:
- Fever
- Cough
- Redness of eyes
- Sensitivity to light
- Pain in muscles
- Runny nose
- White spots in the mouth
- Sore throat
A classic symptom of measles is appearance of widespread rash on the skin. It starts as red bumps that itches and first appears on the head and then gradually spreads to rest of the areas of the body.
Children who have not received the measles vaccine are at risk of developing the disease.
Treatment
There is no medicine that can be prescribed for the treatment of measles. The symptoms usually disappear after 2-3 weeks. Meanwhile, your physician may recommend the following:
- Plenty of rest to boost your immunity
- Acetaminophen to help relieve pain in muscles and fever
- Lots of fluids (at least 6-8 glasses of water every day)
- Air humidifier to relieve sore throat and cough
- Vitamin A supplements
Complications of measles
It is imperative to get a vaccine for measles as it is associated with life-threatening complications including encephalitis and pneumonia. Some other complications of measles are:
- Bronchitis
- Infection of the ear
- Preterm labor or miscarriage
- Reduced blood platelets
- Severe diarrhea
- Blindness
Prevention of measles
Measles can be prevented by getting a vaccine. The MMR vaccine protects children from measles, mumps and rubella. First MMR vaccine is given at the age of 12 months and the second dose is given between the age of four and six years.
-
Roseola
Roseola is another infection that has cough and rash as symptoms. It is a mild infection, which affects children in the age group of 6 months to 36 months. It is caused by infection with human herpes virus 6 or 7. It is a contagious infection and is spread via contact with respiratory secretions of an infected person.
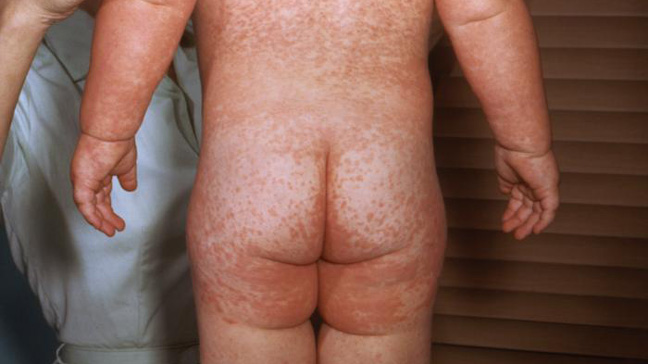
The symptoms of Roseola are:
- Fever. Roseola begins with sudden high temperature, often higher than 103 degree F. Fever may be accompanied by runny nose, sore throat, cough and swollen lymph nodes in the neck. Fever may last for 3-5 days.
- Rash. Rash appears after the fever disappears. It usually begins on chest, abdomen and back and then spreads to arms and neck. The rash is not itchy and may last for several hours or several days.
- Reduced appetite
- Mild diarrhea
- Swelling of eyelids
- Irritability
When to visit a physician
- If the fever is higher than 103 degree F
- If your child has a convulsion
- If the fever does not get better even after 7 days
- If the rash does not get better after 3 days
Treatment
The majority of the children recover from Roseola after a week of beginning of fever. There is no particular treatment available for Roseola, though; some physicians prescribe antiviral ganciclovir in persons with weak immune system.
At the advice of your physician you may give your kid OTC drugs such as Tylenol (acetaminophen) or Advil and Motrin (ibuprofen) to reduce fever.
Prevention of Roseola
Since no vaccine exists to prevent Roseola; the best that can be done to prevent spreading the infection is to avoid the exposure of your child. Moreover, if your child has Roseola, keep them at home and avoid contact with other children until they become well.
Other possible causes of cough and rash:
- Allergies
- Fifth disease
- Asthma
- Drug reaction