In the human body, there are arteries and veins that transport blood through every part of the body. Both are responsible for carrying blood, but they are very different organs. Arteries have different linings and protective coverings from veins and usually carry oxygenated blood away from the heart and to the rest of the body. Veins have thinner walls and usually carry de-oxygenated blood back toward the heart. The difference between arteries and veins usually involves their structural differences and the type of blood they carry.
Difference Between Arteries and Veins
Arteries and veins have different functions and look different when looking at them. These are the main difference between arteries and veins:
Arteries
- They carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to cells all over the body.
- Their walls have 3 layers and are thicker than that of veins.
- They have 2 types of vessels, the pulmonary arteries and systemic arteries.
- Blockage may happen in them, reducing oxygen supply.
Veins
- They carry deoxygenated blood from cells to lungs.
- Their walls are thinner than that of arteries.
- They also have 2 types of blood vessel: the systemic veins and the pulmonary veins.
- Blood clot is a common health condition in veins.
Now let's get the detailed information about all the differences:
1. The Blood They Carry
- Arteries are believed to carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the tissues of the body. The aorta is the main artery that comes out of the heart to oxygenate the body. Oxygenated blood is carried through arteries to every body tissue.
- Veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues to the right atrium, the right ventricle, and finally to the lungs where the lungs take in oxygen and exchange it for carbon dioxide. The blood flows through the pulmonary vein to the left atrium, the left ventricle, and out to the body.
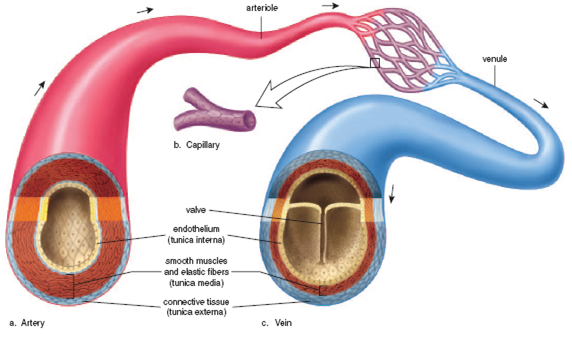
2. Structure
- Artery has three layers, known as the tunica externa, tunica media and tunica interna, which make its walls much thicker than that of veins. The arteries also have no valves and operate under higher pressure than veins.
- Veins have a thinner wall, the thickest layer of which is the tunica adventitia. They contain semilunar valves that keep the blood from flowing backwards as it travels toward the heart and lungs. The pressure of blood inside the veins is lower than in the arteries so the smooth muscles in the venous walls are less well-developed as they are in the arteries.
3. Types of Blood Vessel
One major difference between arteries and veins is that they are different types:
- Arteries consist of two separate types, including the pulmonary arteries and systemic arteries. The systemic arteries always carry oxygenated blood away from the heart and toward the tissues of the body. However, the pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs in order to be given oxygen again.
- Veins have two types of blood vessel: the systemic veins and the pulmonary veins. The systemic veins carry blood that has very little oxygen from the tissues to the heart and lungs. There are superficial and deep systemic veins. But the pulmonary veins carry the oxygenated blood from the lungs into the left atrium of the heart so it can be spread to the body via the arteries.
4. Diseases
- Arteries are prone to getting plaques of cholesterol, known as atherosclerotic arterial vascular disease. Blockage of these arteries can lead to a lack of oxygen to critical parts of the body.
- Veins do not develop cholesterol plaques but can develop thrombosis (blood clots). If they develop in the deep veins, this is called deep vein thrombosis, which can be very dangerous.
How Are Arteries and Veins Connected?
Even though there is a difference between arteries and veins, they are connected to one another. Arteries and vein become smaller and smaller as they extend, and at last they form capillaries. And the capillaries of arteries and veins are connected. This is where the oxygen is exchanged with carbon dioxide in the tissues and where they arteries and veins are connected. After oxygen is exchanged, the blood travels through tiny veins and finally to veins, that carry the blood back to the heart.